CfA Redshift Catalog
The universe is expanding, carrying galaxies with it like flotsam on a fast-flowing river. This expansion also stretches the wavelength of light, which astronomers call cosmological redshift, since it pushes visible light colors toward the red end of the spectrum. That means astronomers can determine the distance to far-away galaxies by measuring the redshift of light they produce. The CfA Redshift Catalog (ZCAT), created by researchers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, is a clearinghouse for historical redshift data from a number of observatories, including the 1.5-Meter Tillinghast Telescope and the MMT Observatory, both CfA-operated telescopes located at the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory (FLWO) in Arizona. This data provides a map of galaxies in three dimensions, allowing astronomers to piece together how galaxies group on the largest scales in the universe. ZCAT is an essential resource for data on redshift surveys up to 2008, carrying on the legacy of the original CfA Redshift Surveys conducted in the 1970s and ‘80s.
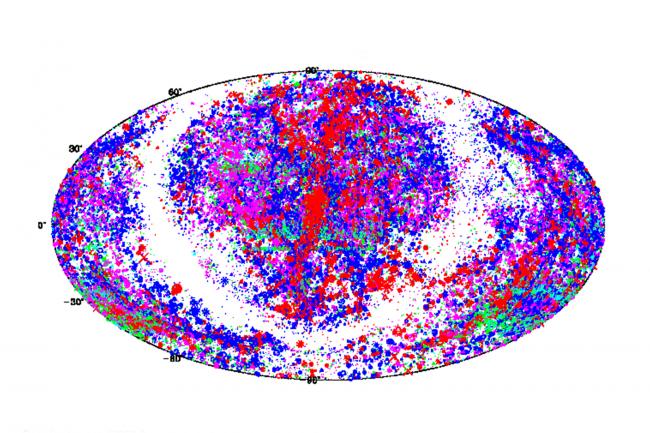
Plot of the distribution on the sky of all entries in ZCAT as of June 2002. Colors are red v < 3000, blue 3000< v < 7000, magenta 7000 < v < 12000, cyan 12000 < v < 25000, and green 25,000 < v < 100,000 km/s. Point size is a function of apparent magnitude. The green bands represent the well studied regions of the LCRS and 2dF surveys and the Century Survey (from a program by J. Mader).
Cosmic Web and Cosmic History
The observable universe contains around 100 billion large galaxies. These are not randomly scattered: they form filaments and other large structures that together create the web-like large-scale structure of the cosmos. The details of that structure trace the behavior of dark matter, and reveal information about the structure and evolution of the universe as a whole.
For astronomers to map the cosmic web, they need to measure the distances to galaxies: the third dimension not provided by a simple map of location on the sky. Cosmological redshift comes to the rescue: because the universe is expanding in a regular, predictable way, redshifts are an excellent proxy for distance. The farther away a galaxy is, the more the cosmos has stretched and the higher the redshift. Starting from the first CfA Redshift Survey in 1977, astronomers have exploited redshift measurements to map the large-scale structure of galaxies. The mathematical symbol for redshift is the letter “z”, so the CfA Redshift Catalog is abbreviated as ZCAT.
ZCAT gathers data gathered from many surveys from 1977 through 2008, providing a single clearinghouse for mapping the cosmos in three dimensions. The catalog — based largely on the Updated Zwicky Catalog (UZC) of galaxies published in 1999 — includes galaxies observed in the two CfA Redshift Surveys, the 2 Degree Field (2df) and 6 Degree Field (6df) redshift surveys conducted in the southern hemisphere, the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), and MMT Hectospec Redshift Survey (MHRS) conducted at the MMT Observatory. Overall, ZCAT includes millions of galaxies, providing a detailed view of the universe and how large-scale structure has evolved over cosmic history.
- Extragalactic Distance Scale
- Large Scale Structure
- Galaxy Formation and Evolution
- Galaxies - Merging and Interacting