Image List
-
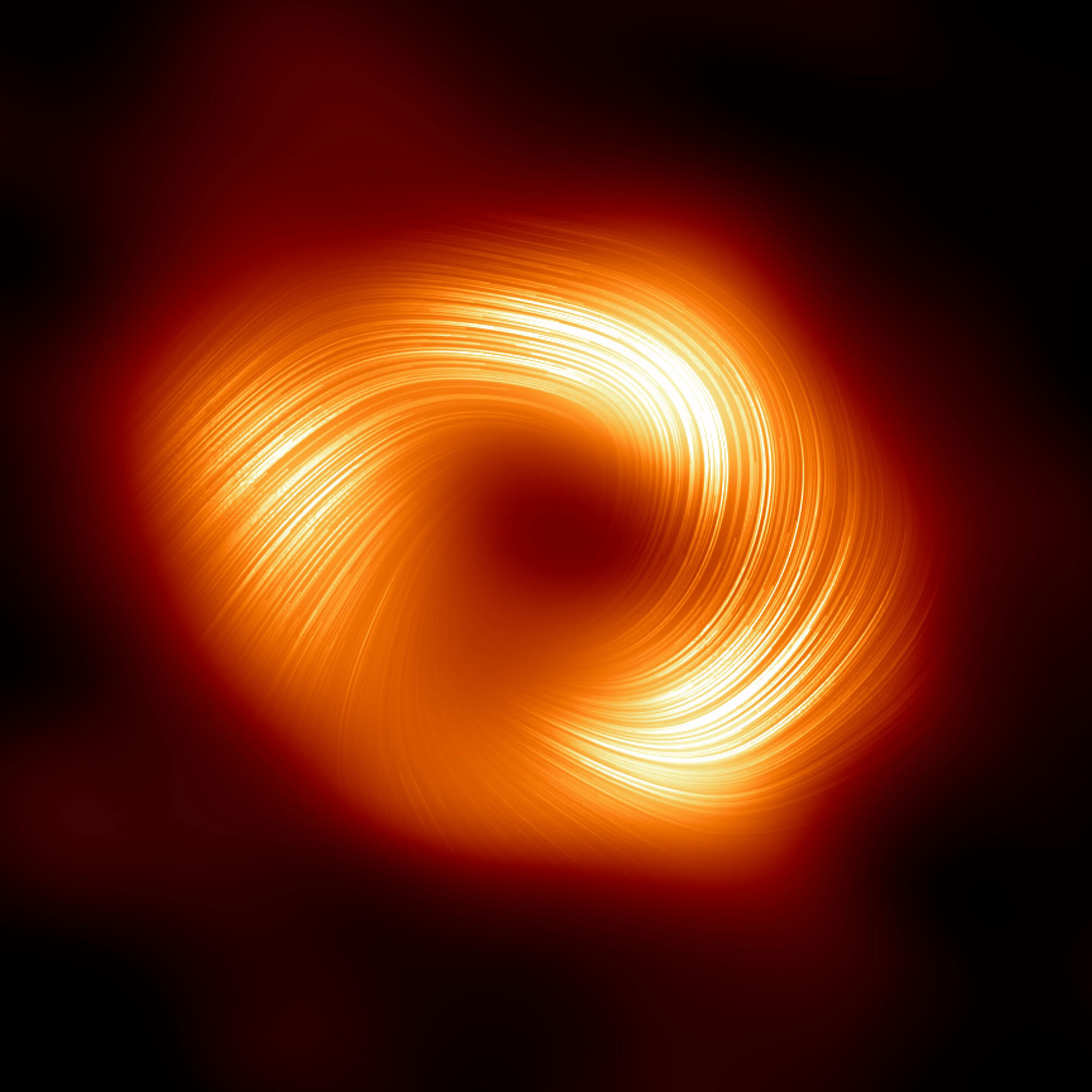

The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration, who produced the first ever image of our Milky Way black hole released in 2022, has captured a new view of the massive object at the center of our Galaxy: how it looks in polarized light. This is the first time astronomers have been able to measure polarization, a signature of magnetic fields, this close to the edge of Sagittarius A*. This image shows the polarized view of the Milky Way black hole. The lines mark the orientation of polarization, which is related to the magnetic field around the shadow of the black hole.
Credit: EHT Collaboration -
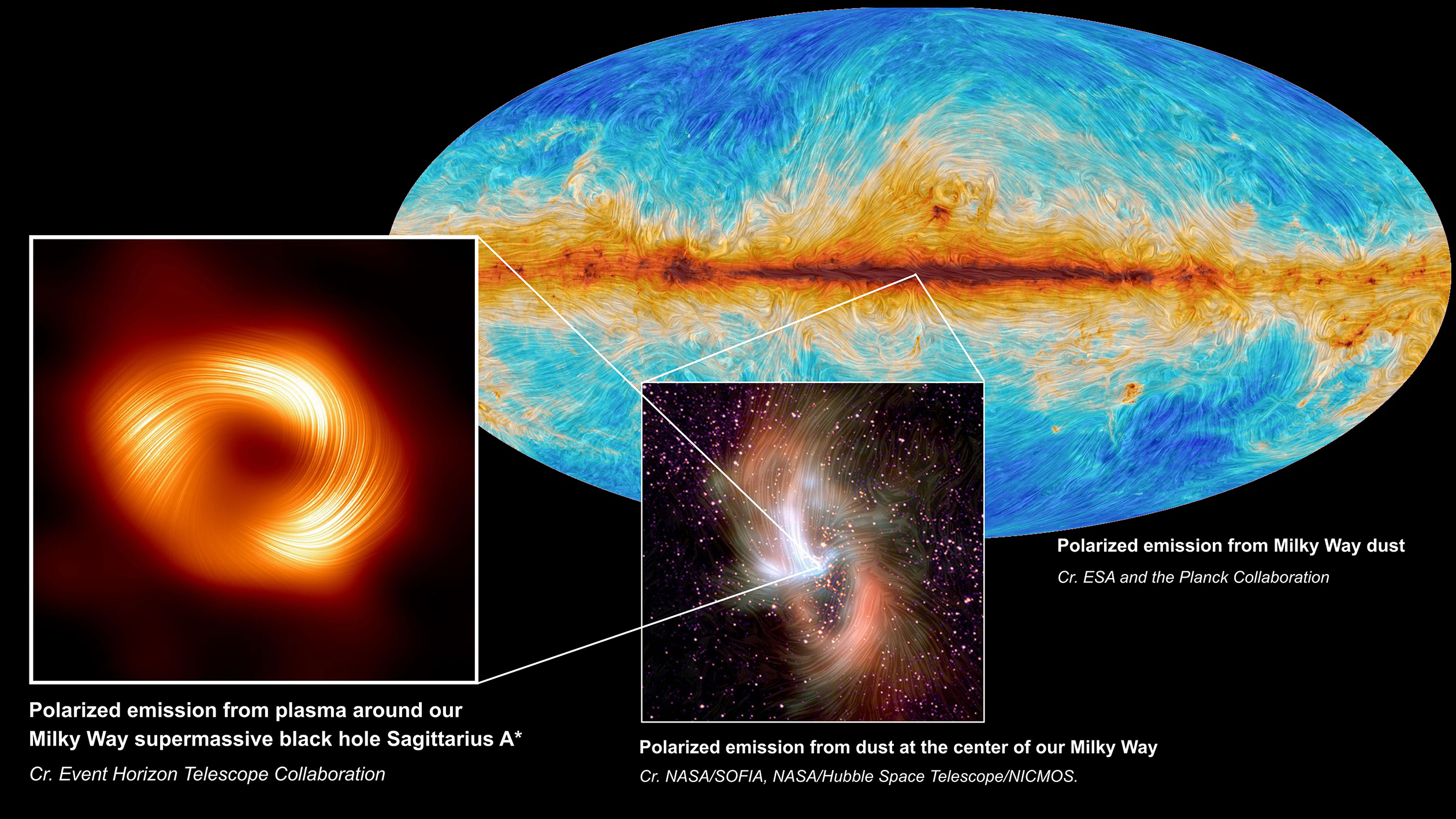
At left, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, Sagittarius A*, is seen in polarized light, the visible lines indicating the orientation of polarization, which is related to the magnetic field around the shadow of the black hole. At center, the polarized emission from the center of the Milky Way, as captured by SOFIA. At back right, the Planck Collaboration mapped polarized emission from dust across the Milky Way.
Credit: S. Issaoun, EHT Collaboration -
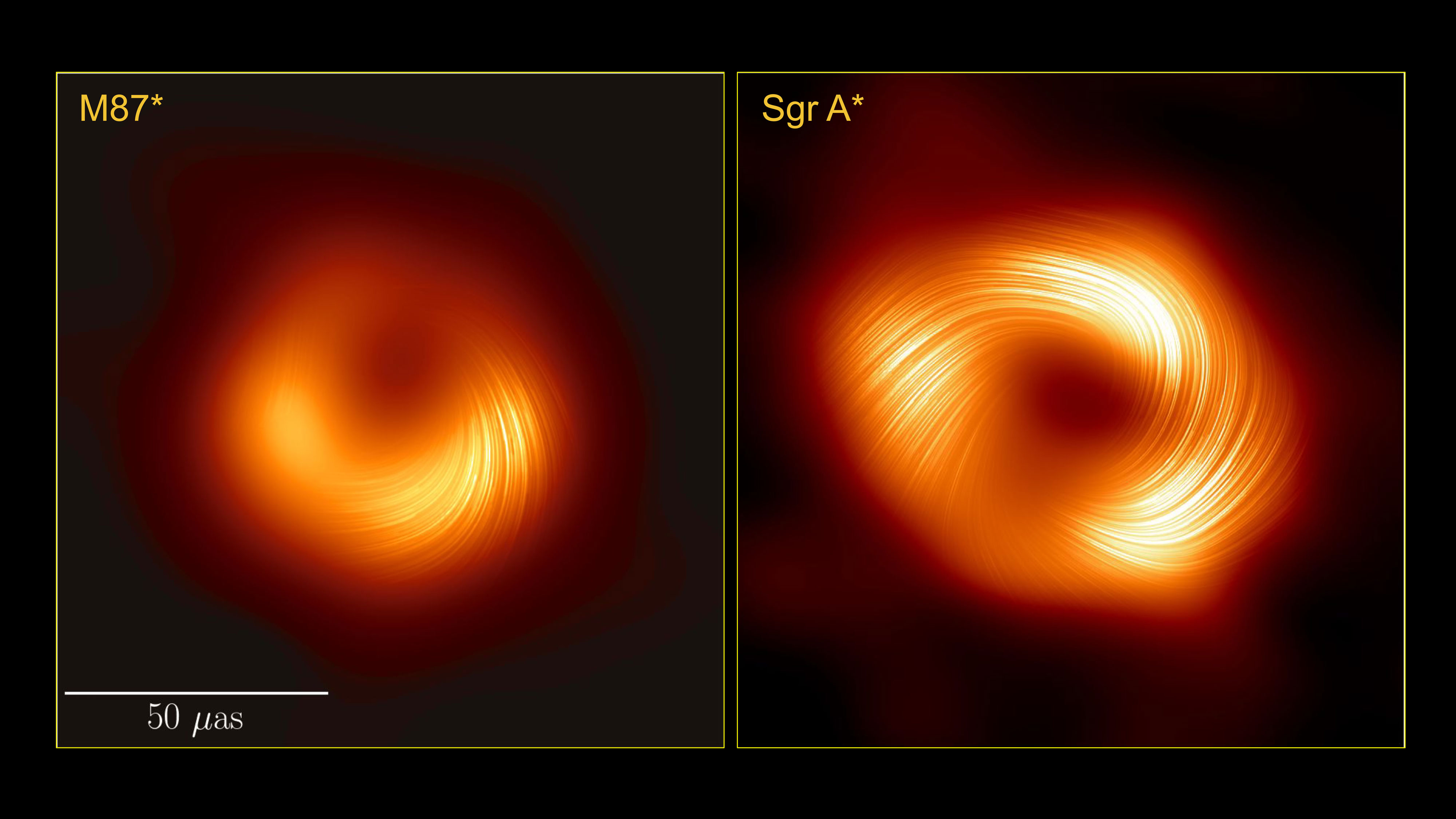
Seen here in polarized light, this side-by-side image of the supermassive black holes M87* and Sagittarius A* indicates to scientists that these beasts have similar magnetic field structures. This is significant because it suggests that the physical processes that govern how a black hole feeds and launches a jet may be universal features amongst supermassive black holes.
Credit: EHT Collaboration