Image List
-
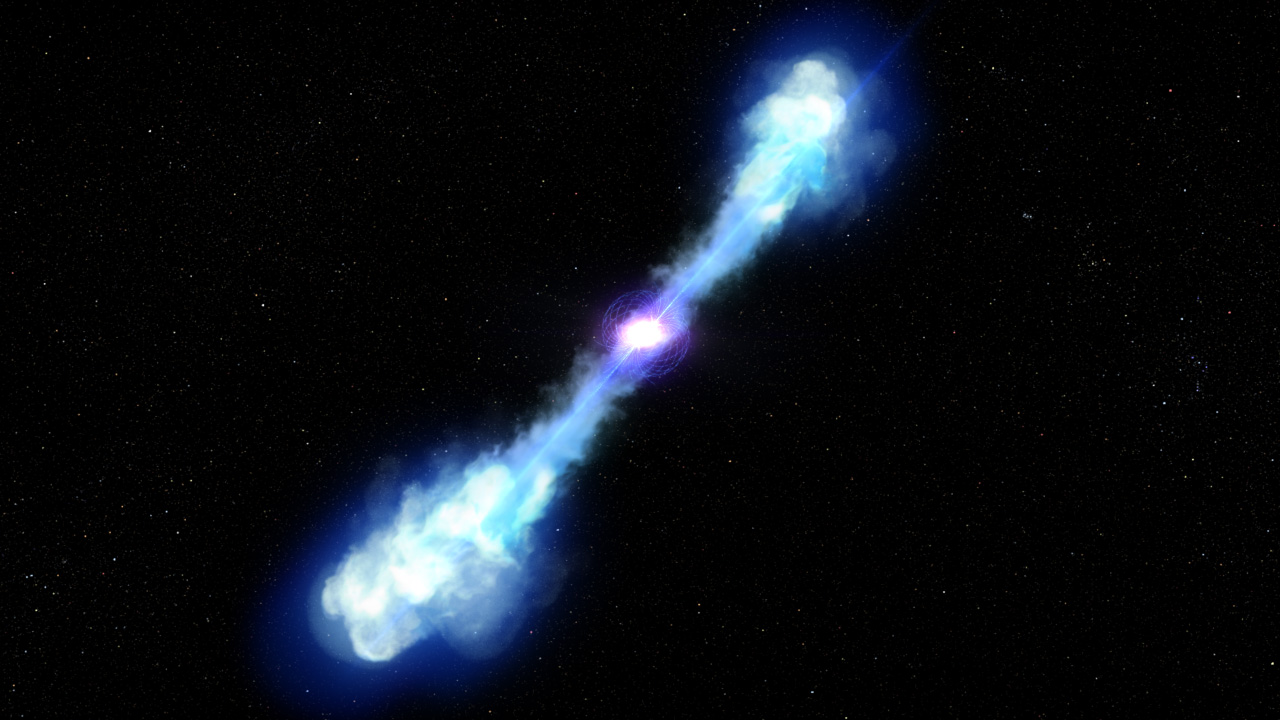
Artist's conception of short gamma-ray burst 200522A, the result of what scientists have confirmed to be the brightest kilonova ever recorded, at ten times brighter than the next closest observed event.
Credit: NASA, ESA, and D. Player (STScI) -
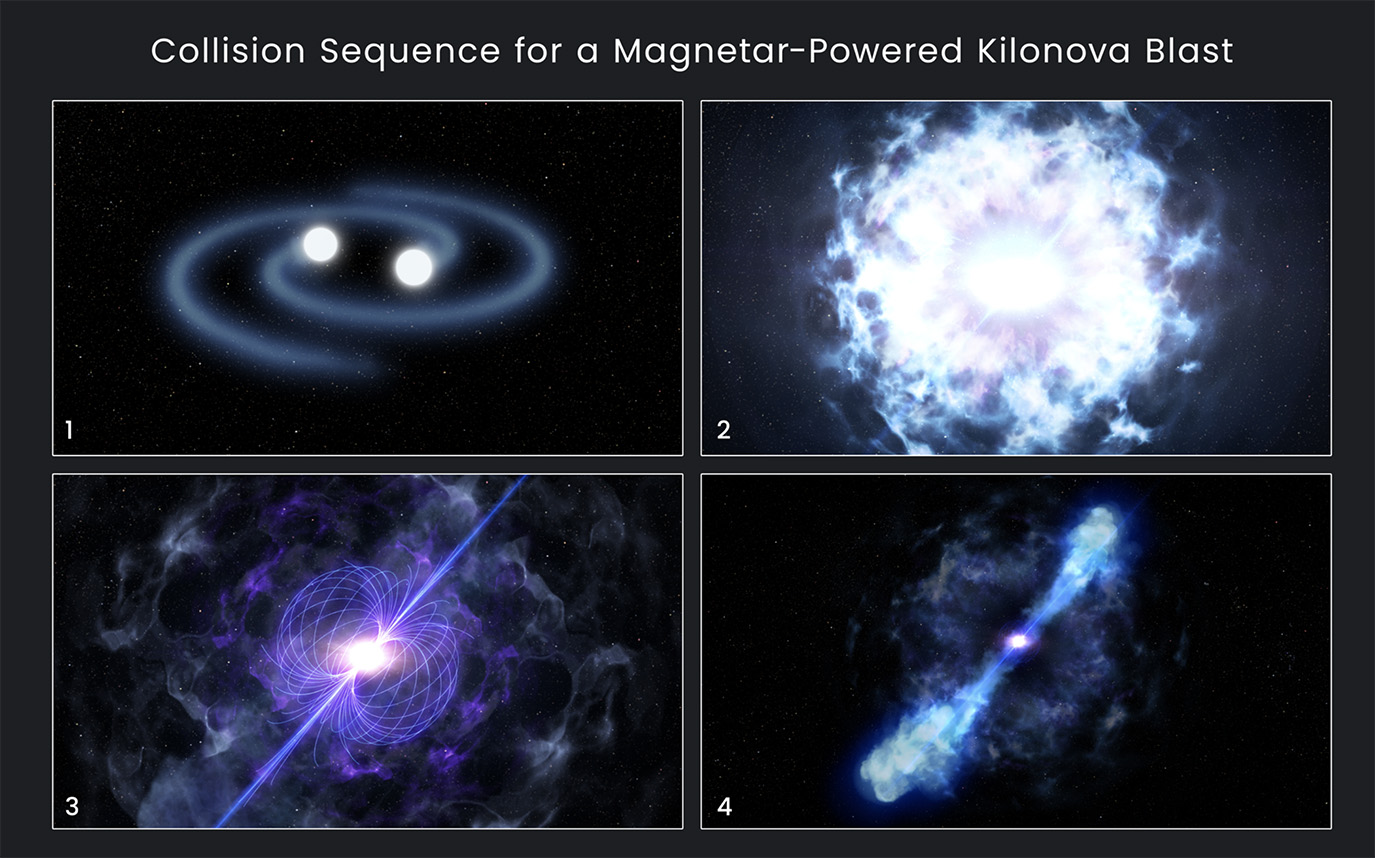
On May 22, 2020, scientists observed what may be the formation of a magnetar--a massive, highly magnetized neutron star. Scientists believe that two neutron stars collided, resulting in a colossal explosion, leaving behind the magnetar as a remnant.
Credit: NASA, ESA, and D. Player (STScI) -
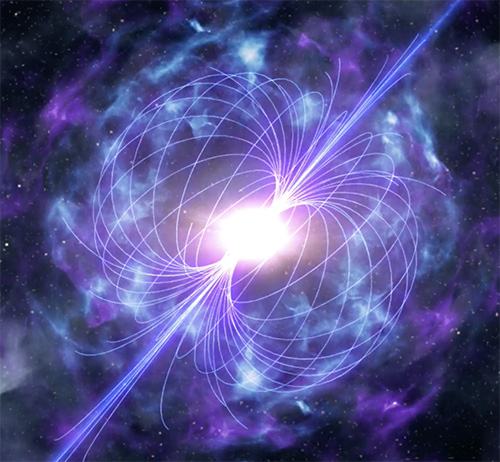
Scientists have long known that short gamma-ray bursts are the result of colliding neutron stars. On May 22, 2020, scientists observed the brightest kilonova ever recorded, leading to further studies which confirm that kilonovae might result in the formation of magnetars--massive, highly-magnetized neutron stars--rather than black holes, as previously theorized.
NASA, ESA, and D. Player (STScI)